|
Spinodal decomposition and secondary phases in VAlN and TiAlN films |
||
|
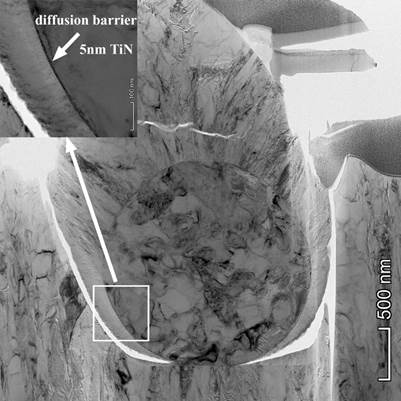
A round macroparticle in the as deposited TiN film formed during arc evaporation. The surface of the particle was covered with a thin c-TiN based diffusion barrier shell which grew in thickness during annealing. |
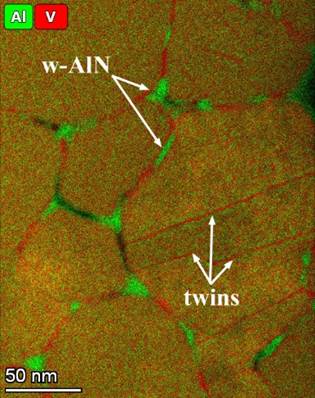
The stability of VAlN and TiAlN hard coatings at high temperatures (900-1100C) is inevitable in applications aiming at increasing the lifetime of tools. The VAlN and TiAlN layers were deposited by reactive sputtering and cathodic arc evaporation, respectively, at Aachen University. The TEM/STEM investigations were made on the CS corrected Themis microscope of MFA. Spinodal phase separation of V (Ti) and Al rich fcc nitride phases was observed in both material systems by EDS elemental maps on 8-20 nm scale and by electron diffraction for TiAlN. In VAlN the hexagonal AlN phase was observed above 800C which forms at the grain boundaries according to EDS elemental maps (right), HRTEM and dark field images. Self-organized formation of a c-TiN based diffusion barrier shell was observed around TiAlN macroparticles (left), formed in cathodic arc evaporation, providing unexpected stability at high temperature of 1000C. |
Phase separation
in VAlN film: Parallel with spinodal
decomposition, Al diffuses to grain boundaries and concentrates at triple
junctions to form w-AlN. On the other hand twin
boundaries are Al depleted. |